Home solar power system and approximate cost of cost

- news
- 0
Home solar power system and approximate calculation of its cost
A solar PV system consists of different parts that should be selected according to the application, location and type of system. By building home power plants, you can supply the electricity you need through solar energy. There are two types of home power plants. One for selling electricity to the grid and the other for self-consumption.
Renewable service: The sun as an endless source of energy can be a solution to problems in the field of energy and environment. Unfortunately, cheap energy and high bank interest both make it not cost-effective to spend on solar power systems in our country, while in the long run these systems are very cost-effective and have a significant impact on reducing air pollution. will also have
Solar systems for public and agricultural use are used as power plants independent of the national grid or systems connected to the national grid with a fixed or mobile installation structure in small units with low power to supply the electrical energy required from small calculators to large power plant systems.
Each square meter of the surface that the sun shines on on a day without clouds and pollution receives about 1000 watts of radiant power. The average amount of radiation in Iran is about 950 watts per square meter. The solar panels available in the commercial market have an efficiency of about 17-22% and considering that the entire surface of a solar panel does not contain energy-receiving silicon, each square meter of these panels can receive about 150-300 watts of energy. Of course, it should be noted that this amount of energy is in the case of perpendicular sunlight to the panel, and the angle of the panels must be adjusted in different seasons of the year. Commercial solar panels are generally above 300 watts.
Types of solar power system used in a house:
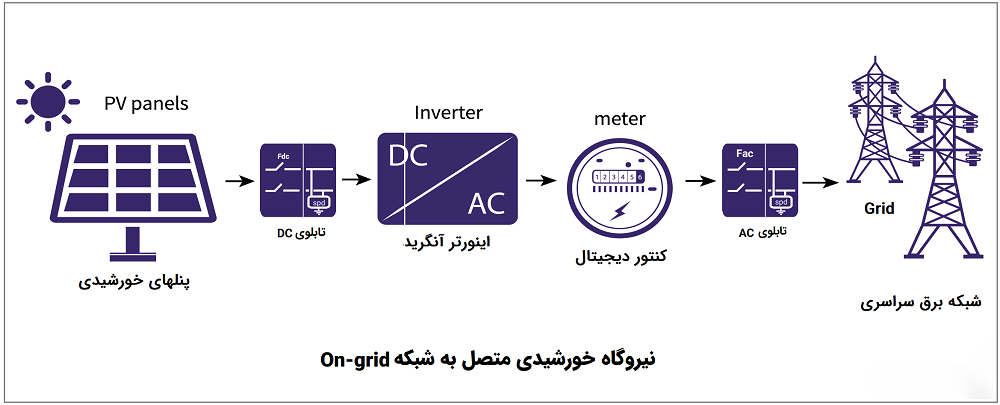
1- Connected to the grid (On Grid): In the system connected to the grid, electricity produced from solar energy will be injected into the national grid. In fact, in this system, the user sells his produced electricity to Iran’s Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Organization (SATBA), which is a government agency. In this method, the generated electricity will be injected into the national electricity grid after being converted by the special inverter of the systems connected to the grid and using special meters. In this case, the user has actually built a small solar power plant in his home, which can build a power plant from 1 to 200 kilowatts at home, depending on the capital and space.
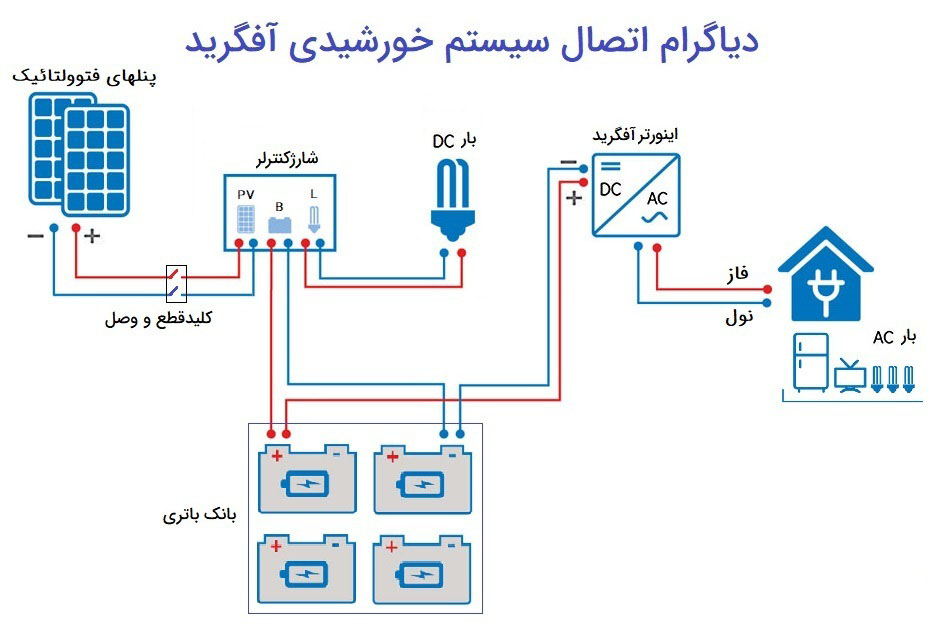
2- Off Grid: In this type of system, the electricity generated from the solar panel enters the battery and is stored in it. Then, the electricity stored in the battery after being converted into alternating current by the inverter for off-grid systems, enters the house’s electrical circuit. In this method, a user can supply all or part of his home’s electricity using solar electricity. In the following, the explanation of the off-grid solar power system and the cost estimate for a house will be discussed.
The components of the photovoltaic system are:
Panel (photovoltaic cells): these cells are thin squares of disks or films of semiconductor materials that produce sufficient voltage and current when exposed to sunlight. Conventional solar panels are divided into two types: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Mono crystal panels are slightly better than poly crystal panels.
The usual panels for a home solar system are 250 and up to 500 watts. Their dimensions are 2 meters by 1 meter (or 1.7 meters by 1 meter) and they are divided into two types, monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
Solar panels or solar panels are used to produce electrical energy in the solar power plant. An expensive high-efficiency panel may perform just as well as a standard or affordable panel under the same conditions. To choose a solar panel, parameters such as the quality of sunlight, installation angle, temperature coefficient, etc. must be examined.
In the type connected to the grid, the electricity produced from the solar panel is directly entered into the inverter. Therefore, this inverter is different from ordinary inverters. Because the electricity generated from the panel is always changing due to the effects of environmental conditions such as changes in sunlight. So the inverter does not face a uniform input power, and as a result, it must have a special pattern to convert direct current to alternating current. As a result, the price of the solar inverter is higher than the normal inverter.
In the off-grid type, the inverter converts the electricity stored in the battery from 12 V direct to 220 V alternating to make it suitable for use in home appliances. The more sinusoidal the inverters are, the better they will be. These inverters are not like grid connected inverters because they will convert uniform power from the battery.
To choose an inverter, two very important parameters should be considered:
the input voltage to the inverter and the output power from the inverter.
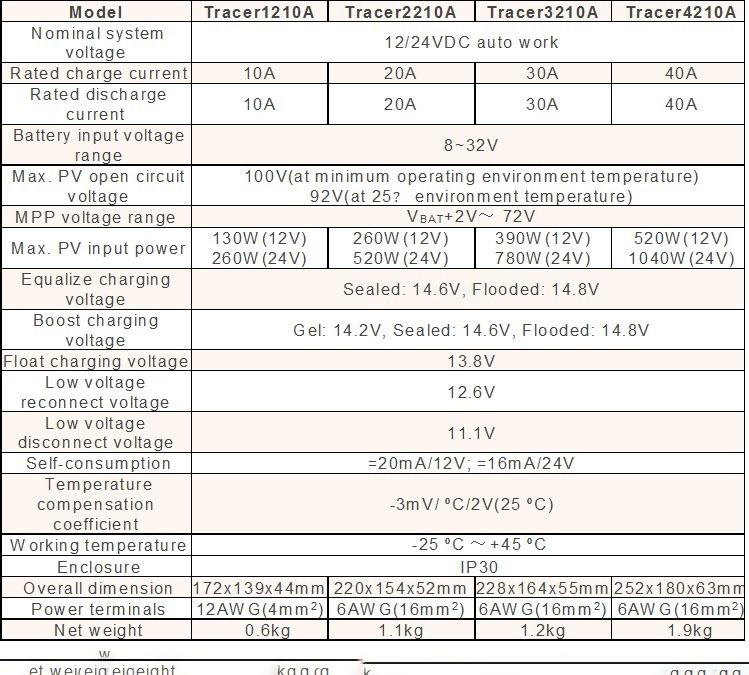
The input voltage to the inverter disconnected from the network is related to the battery voltage, and in the type connected to the network, it is related to the panel voltage. The output power from the inverter is related to the maximum power for which the system is designed. This power for off-grid systems usually ranges from 200 watts to 7000 watts in inverters.
The following table shows the technical specifications of several inverters.

Charge controller: The charge controller is responsible for charging the batteries from the solar panel source. In fact, the charging controller is the same as the battery charger, but the charging of the solar controller must follow the charging pattern of a battery (it is worth mentioning that the charging of the lead acid battery controller is different from the lithium battery and this is due to the difference in the charging pattern of these two batteries) ) should also adapt to the variable power of a solar panel. From this point of view, charging the solar controller is also more expensive than a regular charging controller.
To choose charge controllers, two parameters of battery voltage and panel power should be taken into account.
Some suitable solar controller charging models are EP Solar, Carspa and Phocos.
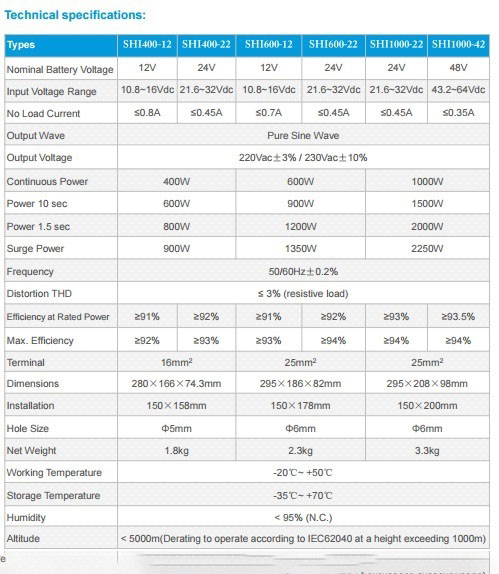
Charge controllers have different types based on voltage (usually 12 or 24 volt direct input) and output power or current (from 5 amps to 40 amps), but generally they can be divided into two categories: PWM and MPPT. In the MPPT model, the charge controller will work at maximum power by adopting a pattern that always changes in the voltage and current generated from the solar panel. Therefore, the MPPT model is more expensive than the PWM model.
The following table shows the technical specifications of several charge controllers.
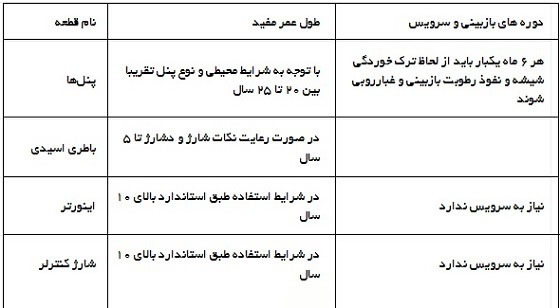
Battery: The last component of an off-grid solar system is the power storage source produced by the solar panel, which is the same as rechargeable batteries.
Suitable batteries for the solar system are divided into two types: lithium and lead acid. Of course, acid batteries are used for a solar system required by a house. Currently, common lead acid batteries are of gel type.
The table below shows the lifespan of the used parts.
Calculating the cost of supplying electricity to the house using the solar system
is the calculation of the amount of power of the solar cells, considering the geographical location where the photovoltaic panels are supposed to be installed, it is of considerable importance. Because in different geographical locations, parameters such as the angle of sunlight, the average daily sunlight, the amount of cloudy days throughout the year and other atmospheric and environmental factors will have a great impact on the design of the panels in terms of capacity.
Calculations and formulas are explained in simple language and the book is written in such a way that it can be understood by the general public. All modifications and technical parameters are explained. The electricity consumption table of different equipment is presented in full and the chapter related to solar water pumps is presented in a practical way to meet the needs of the audience.
The most important parameter that affects the capacity of panels in different geographical conditions is the average daily sunlight in a region in terms of hours. Fortunately, in this sense, Iran is a country that spends most of the days of the year sunny, and the annual average of sunny days in Iran, especially in the central regions, is very high.
To calculate the required power, the energy consumption of the house must be obtained first. This amount is included on the electricity bills, and each user can get his average monthly consumption through his electricity bill. But on average, for a 90-meter house, this amount is about 165 kilowatt-hours per month, or in other words, about 5.5 kilowatt-hours per day. Of course, in the summer days when the air conditioner will be turned on, this amount will increase and the type of water or gas air conditioner consumes different power. Now, if a user wants to use solar power for his home, he should get his daily consumption power according to the electrical appliances.
According to the experimental data obtained from a solar power plant in Tehran, a 250 watt solar panel can produce electricity between 1200 and 1700 watt hours per day on average; Therefore, in order to provide the minimum electricity required for a house, 4 solar panels of 250 watts or in other words one kilowatt panel should be used. In this case, approximately 3,800 to 4,800 watt hours of electricity will be produced per day.
Source: Journalists Club




